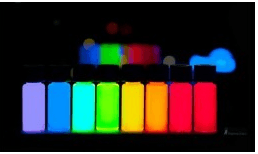
The Dawn of a New Diagnostic Era: What Are Quantum Dots?
Imagine a world where diseases are detected at their earliest stages from a single drop of blood, where medical tests are faster, more sensitive, and accessible to all. This is the world that Quantum Dots (QDs) are helping to build. At their core, QDs are minuscule semiconductor nanocrystals, so small that they operate under the bizarre and wonderful laws of quantum mechanics. Their most celebrated feature is their fluorescence—a brilliant, stable glow when illuminated with UV light. Unlike traditional fluorescent dyes that have broad, overlapping signals and fade quickly, QDs offer sharp, size-tunable colors that shine bright and long.
For the vibrant R&D landscape in India, this technology isn't just a scientific curiosity; it's a paradigm shift. As the nation strives for self-reliance in healthcare and biotechnology, the need for advanced diagnostic tools has never been more pressing. A highly sensitive QD assay can detect biomarkers for cancer, infectious diseases, and genetic disorders with unparalleled precision. This move towards nano diagnostics represents a significant leap, enabling the development of sophisticated yet cost-effective diagnostic tests that can be deployed across the country, from high-tech urban labs to rural point-of-care settings. The adoption of the fluorescence assay based on QDs is a critical step in strengthening India's public health infrastructure.
Why Every Indian Researcher Should Be Excited About QD Assays
The transition from conventional organic fluorophores to quantum dots in a diagnostic test is not merely an upgrade; it's a complete overhaul of our capabilities. For researchers and clinicians in India, the benefits are tangible and transformative:
- Unmatched Photostability: QDs are incredibly resistant to photobleaching. This means they can be imaged for longer periods without signal loss, allowing for more rigorous analysis and real-time tracking in complex biological systems—a crucial feature for any advanced bioassay enhancement.
- Superior Multiplexing: Thanks to their narrow and distinct emission spectra, different-colored QDs can be used simultaneously to detect multiple targets in one sample. A single QD bioassay could screen for a panel of cancer markers or different viral strains, saving time, resources, and patient samples.
- Exceptional Sensitivity: QDs have a very high quantum yield (they are very bright) and a high signal-to-noise ratio. This allows for the detection of molecules at extremely low concentrations, enabling earlier disease diagnosis and more effective medical testing.
- Simplified Excitation: A key advantage of QDs is their broad absorption spectrum. This means a single light source (e.g., a UV or blue laser) can be used to excite a full range of different-sized QDs, each emitting its own specific color. This simplifies the design and cost of diagnostic instruments.
- Tunable Optical Properties: The color of light a QD emits is directly related to its size. This allows scientists to produce a rainbow of fluorescent probes, perfectly tuned for specific applications, making the QD diagnostic platform incredibly versatile.
Real-World Impact: Applications of Quantum Dot Diagnostics
The theoretical benefits of QDs translate into powerful, real-world applications that are particularly relevant to India's health challenges. The versatility of the nano assay powered by QDs is reshaping multiple fields.
Oncology and Cancer Research
QDs are used as fluorescent labels for antibodies that target specific cancer biomarkers, like PSA for prostate cancer or HER2 for breast cancer. This allows for highly sensitive imaging of tumors and the detection of circulating tumor cells in blood, paving the way for non-invasive liquid biopsies.
Infectious Disease Diagnostics
In a country battling diseases like tuberculosis, dengue, and chikungunya, rapid and accurate diagnosis is key. A multiplexed QD assay can be designed to simultaneously detect antigens or nucleic acids from multiple pathogens, providing a comprehensive diagnostic picture in a fraction of the time of traditional methods.
Cellular Imaging and Tracking
The photostability of QDs makes them ideal for long-term live-cell imaging. Researchers can track cellular processes, protein trafficking, and drug delivery mechanisms in real-time without the fear of the fluorescent signal fading, offering deep insights into fundamental biology.
Environmental Toxin Sensing
Beyond medicine, nano diagnostics have a role in environmental safety. QD-based biosensors can be developed to detect heavy metals, pesticides, and other pollutants in water and soil with high sensitivity, contributing to public health and environmental monitoring efforts.
The Indian Landscape: Opportunities and the Path Forward
The convergence of India's burgeoning biotechnology sector and national initiatives like "Make in India" and the "National Health Mission" creates a fertile ground for nano diagnostics. The demand for indigenous, affordable, and high-quality diagnostic kits is at an all-time high. Investing in R&D for QD assay platforms aligns perfectly with these national priorities. Indian scientists and startups are increasingly exploring how to leverage quantum dots for enhancing photocatalytic reactions and biomedical assays, aiming to reduce import dependency and create globally competitive products.
However, the journey involves overcoming challenges. Widespread adoption requires standardization of protocols, addressing regulatory hurdles, and managing the potential toxicity of early-generation cadmium-based QDs. This is where the focus is shifting towards safer, cadmium-free alternatives like InP/ZnS or carbon quantum dots. The development and local manufacturing of these safer materials are critical for the long-term success of the QD diagnostic field in India.
The future lies in integrating these advanced materials into user-friendly platforms. Imagine a simple, paper-based lateral flow assay (like a pregnancy test) but with the sensitivity and multiplexing power of a fluorescence assay using QDs. Such devices could revolutionize community health screenings. By fostering collaboration between academic research institutions, industry, and government bodies, India can cement its position as a leader in the field of nano assay technology and advanced medical testing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Quantum Dots are semiconductor nanocrystals, typically between 2-10 nanometers in size. Their tiny size gives them unique quantum mechanical properties, most notably the ability to emit light of specific colors when excited by UV light. The color they emit depends directly on their size, allowing for highly tunable and precise fluorescence.
This is a key area of research. Traditional QDs often contain heavy metals like cadmium, raising toxicity concerns. However, modern advancements include encapsulating these QDs in a protective, biocompatible shell (like Zinc Sulfide) to prevent leakage. Furthermore, the development of cadmium-free QDs, such as those based on indium or zinc, is a major focus in the field, offering safer alternatives for in-vivo and clinical applications.
QD assays offer several advantages. They are extremely photostable, meaning they don't 'bleach' or fade under prolonged light exposure like organic dyes. They have narrow, symmetric emission peaks, which prevents signal overlap and allows for 'multiplexing'—detecting multiple targets in a single sample. Their broad absorption spectra also mean you can excite a whole panel of different-colored QDs with a single light source, simplifying instrumentation.
Indian researchers can source high-quality, research-grade quantum dots from specialized suppliers like Hiyka, which offers a wide range of QDs, including hydrophilic, hydrophobic, and cadmium-free options suitable for various diagnostic and research applications. They provide materials tailored for the Indian R&D ecosystem.
Nano diagnostics are crucial for India as they pave the way for developing low-cost, high-sensitivity, point-of-care diagnostic tests. This is vital for early disease detection in remote and resource-limited settings. By leveraging technologies like QD assays, India can address public health challenges more effectively, from infectious diseases to cancer screening, aligning with national initiatives like 'Make in India' and 'Ayushman Bharat'.