The Dawn of a New Diagnostic Era in India
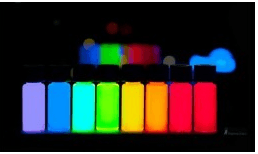
In the bustling landscape of Indian research and development, a nanotechnology revolution is quietly unfolding. At its heart are Quantum Dots (QDs)—minuscule semiconductor particles, merely a few nanometers in size, that are poised to redefine medical diagnostics. For researchers and professionals across India, from the labs of Bangalore to the pharmaceutical hubs of Hyderabad, understanding the power of QDs is no longer optional; it's essential. These nanocrystals are not just a scientific curiosity; they are the foundation for the next generation of **QD diagnostic** tools, offering unprecedented sensitivity and specificity in **disease detection**.
The core challenge in modern medicine is early and accurate diagnosis. Traditional methods, while effective, often lack the sensitivity to detect diseases at their nascent stages. This is where the unique quantum mechanical properties of QDs come into play. When excited by light, they emit brilliant, stable colors that are dependent on their size. This phenomenon makes them perfect candidates for **fluorescence imaging** and **bioimaging**, allowing scientists to visualize cellular processes with stunning clarity. A **QD medical sensor** can be designed to light up in the presence of a specific cancer biomarker or a virus, providing a clear, unmistakable signal. This technology represents a monumental leap from conventional diagnostic assays, paving the way for a future where diseases are caught sooner, treated more effectively, and managed more personally.
Why Researchers are Turning to Quantum Dots
The advantages of integrating QDs into diagnostic platforms are compelling, offering solutions to many limitations of traditional fluorophores.
-
Exceptional Photostability
Unlike traditional organic dyes that fade quickly, QDs are highly resistant to photobleaching. This allows for long-term imaging and tracking of biological processes, crucial for studying disease progression and treatment response.
-
Multiplexing Capabilities
A single light source can excite QDs of different sizes, each emitting a distinct, sharp color. This allows for the simultaneous detection of multiple biomarkers in a single sample—a process known as multiplexing. This is a game-changer for complex **disease detection** like cancer, where multiple genetic markers need to be assessed.
-
High Quantum Yield & Brightness
QDs are incredibly efficient at converting light, making them significantly brighter than conventional probes. This high signal-to-noise ratio enables the detection of molecules at extremely low concentrations, pushing the boundaries of early diagnosis.
-
Tunable Emission Spectra
By simply changing the size of the quantum dot, researchers can tune its emission wavelength from blue to near-infrared. This precise control over color is fundamental to designing a specific **QD assay** for any target molecule.
Key Applications in Medical and Environmental Fields
Advanced Bioimaging and Cellular Tracking
The use of QDs in **fluorescence imaging** is transforming our ability to observe life at the nanoscale. Researchers can conjugate QDs with antibodies or peptides, directing them to specific cellular structures like the nucleus or mitochondria. This allows for real-time visualization of dynamic processes, such as viral entry into cells or the metastasis of cancer cells. This level of detail is invaluable for understanding disease mechanisms and developing targeted therapies.
Highly Sensitive In-Vitro Diagnostics
QD-based immunoassays are emerging as a powerful **nano diagnostic tool**. By replacing traditional enzymes or dyes in formats like ELISA, QDs dramatically increase the sensitivity of these tests. A **QD assay** can detect picomolar concentrations of disease biomarkers, from cardiac troponins for heart attack diagnosis to viral antigens for infectious diseases. This leads to earlier and more reliable diagnoses from blood or saliva samples.
Point-of-Care Diagnostic Devices
The stability and brightness of QDs make them ideal for robust, portable diagnostic devices. Imagine a handheld **QD medical sensor** that a healthcare worker in a rural Indian village could use to test for malaria or dengue with just a drop of blood. This is the promise of **QD health tech**—democratizing diagnostics and bringing advanced medical testing to the point of need, a critical goal for India's healthcare infrastructure.
Quantum Dots for Enhancing Environmental Sensors
Beyond medicine, QDs are enhancing environmental monitoring. Sensors integrated with quantum dots can detect minute quantities of heavy metals like mercury and lead, or organic pollutants in water sources. Their high sensitivity provides an early warning system against contamination, crucial for ensuring public health and environmental safety across India's industrial and agricultural regions.
The Indian Horizon: Opportunities and Research Trends
India, with its burgeoning biotech sector and world-class research institutions, is uniquely positioned to become a global leader in **QD health tech**. The 'Make in India' initiative provides a fertile ground for developing indigenous **nano medical devices** and diagnostic kits. The focus is shifting from theoretical research to tangible applications that can solve India-specific health challenges.
A major trend is the development of low-cost **QD diagnostic** platforms for endemic infectious diseases. Researchers at institutions like the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) and the Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CCMB) are actively working on QD-based biosensors for tuberculosis, HIV, and hepatitis. The goal is to create rapid tests that are not only accurate but also affordable and accessible to the wider population.
Furthermore, the application of **bioimaging** using quantum dots in cancer research is gaining significant traction. Scientists are using QDs to understand tumor heterogeneity and to develop targeted drug delivery systems where the QD acts as both an imaging agent and a vehicle for therapeutics. This dual-functionality is at the forefront of personalized medicine, a field where India is poised to make significant contributions. The development of cadmium-free, biocompatible quantum dots is another key research area, addressing toxicity concerns and paving the way for safe in-vivo applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ready to Advance Your Research?
Explore our comprehensive range of high-quality quantum dots and accelerate your next breakthrough in diagnostics and bioimaging.
Browse All Quantum Dots